Introduction
In the realm of electric motors, the design and manufacturing of stators play a pivotal role in determining performance and efficiency. One innovative approach gaining traction is the hairpin stator design. This article aims to provide a comprehensive review of hairpin stator manufacturing, shedding light on its intricacies, applications, and future prospects.
Understanding the Hairpin Stator Design
Benefits of Hairpin Stator Design
The hairpin stator design offers several advantages over traditional designs. Its compact structure enhances power density, leading to lighter and more efficient electric motors. Additionally, the reduced copper content contributes to cost savings and improved thermal management.
Comparison with Traditional Stator Designs
In contrast to conventional windings, which utilize round wire coils, hairpin stators employ pre-formed copper conductors. This design minimizes end-turn losses and enhances coil fill factor, resulting in superior performance and longevity.
Materials Used in Hairpin Stator Manufacturing
Hairpin stators utilize high-quality materials to ensure durability and reliability.
Copper Alloys
Copper alloys with excellent conductivity are preferred for hairpin stator windings. These alloys offer superior electrical and mechanical properties, enabling optimal motor performance.
Insulation Materials
Insulation materials such as epoxy resins are crucial for protecting copper conductors from environmental factors and electrical stress. Advanced insulation techniques ensure long-term insulation integrity and motor reliability.
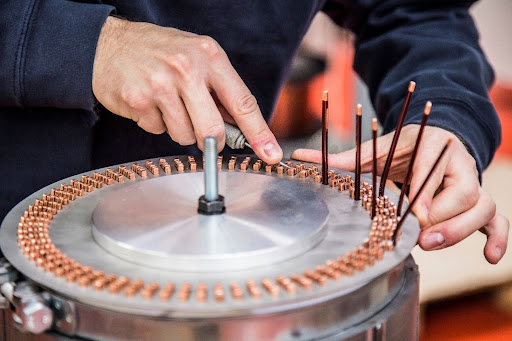
The Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of hairpin stators involves several intricate steps.
Coil Winding
Precision coil winding machines carefully wind copper conductors into hairpin shapes, maintaining consistent winding tension and geometry.
Forming the Hairpin Shape
Specialized forming equipment shapes the wound coils into hairpin configurations, optimizing electrical conductivity and thermal dissipation.
Insulation Application
Insulation materials are meticulously applied to the hairpin coils, safeguarding against electrical faults and environmental degradation.
Final Assembly
The assembled hairpin stators undergo rigorous quality checks before integration into electric motors or generators.
Quality Control Measures
Ensuring the quality of hairpin stators is paramount to their performance and reliability.
Testing Procedures
Comprehensive testing protocols, including insulation resistance tests and dielectric strength tests, validate the integrity of hairpin stator windings.
Ensuring Efficiency and Reliability
Stringent quality control measures and adherence to industry standards guarantee the efficiency and reliability of hairpin stator assemblies.
Applications of Hairpin Stators
Hairpin stators find applications across various industries, including automotive, renewable energy, and industrial sectors.
Automotive Industry
In electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid vehicles, hairpin stators power propulsion systems, delivering high torque and efficiency.
Renewable Energy Sector
Hairpin stators drive the generators in wind turbines and hydroelectric plants, harnessing renewable energy with unmatched efficiency.
Industrial Machinery
In industrial applications such as pumps, compressors, and conveyors, hairpin stators offer reliable and energy-efficient operation.
Advancements in Hairpin Stator Technology
Continuous advancements in manufacturing techniques drive innovation in hairpin stator technology.
Innovations in Manufacturing Techniques
Advanced automation and precision machining enable the cost-effective production of high-performance hairpin stator assemblies.
Future Prospects
Ongoing research aims to further enhance the performance and sustainability of hairpin stators, paving the way for widespread adoption in diverse applications.
Challenges and Solutions
Despite its many benefits, hairpin stator manufacturing faces challenges such as cost constraints and technical limitations.
Cost Considerations
The initial investment required for specialized equipment and materials can pose challenges for manufacturers.
Technical Challenges
Achieving uniform coil winding and precise insulation application requires continuous refinement of manufacturing processes.
Environmental Impact
Hairpin stator manufacturing endeavors to minimize its environmental footprint through sustainable practices and recycling efforts.
Sustainability Practices
Efforts to reduce energy consumption and waste generation contribute to the environmental sustainability of hairpin stator production.
Recycling Efforts
Recycling initiatives aim to recover and reuse materials, minimizing resource depletion and waste generation.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Real-world applications demonstrate the effectiveness and reliability of hairpin stators in diverse environments.
Real-world Applications
Case studies highlight successful implementations of hairpin stator technology in various industries, showcasing its versatility and performance.
Industry Successes
Success stories from leading manufacturers underscore the transformative impact of hairpin stators on electric motor performance and efficiency.
Training and Skill Requirements
Developing a skilled workforce is essential for the successful adoption and implementation of hairpin stator technology.
Developing a Skilled Workforce
Training programs and educational initiatives equip professionals with the knowledge and expertise to manufacture and maintain hairpin stators effectively.
Educational Programs
Collaborations between industry stakeholders and educational institutions foster the development of specialized skills required for hairpin stator manufacturing.
Market Trends and Growth Opportunities
The global market for hairpin stators is poised for significant growth, driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient electric motors.
Global Market Analysis
Market research indicates a rising adoption of hairpin stator technology across key industries, fueling market expansion and innovation.
Forecasted Growth
Projections suggest sustained growth in demand for hairpin stator assemblies, driven by advancements in electric vehicle technology and renewable energy infrastructure.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Adherence to regulatory standards is essential to ensure the safety and reliability of hairpin stator assemblies.
Industry Regulations
Compliance with industry regulations and certification requirements is imperative for manufacturers to maintain product quality and integrity.
Compliance Requirements
Stringent quality control measures and documentation practices facilitate compliance with regulatory standards and customer specifications.
Future Outlook
The future of hairpin stator manufacturing is promising, with continued advancements poised to drive innovation and growth.
Emerging Technologies
Technological breakthroughs such as additive manufacturing and advanced materials hold the potential to further enhance the performance and efficiency of hairpin stators.
Anticipated Developments
Anticipated developments in automation and digitalization are expected to streamline manufacturing processes and increase production efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hairpin stator manufacturing represents a significant advancement in electric motor technology, offering numerous benefits in terms of efficiency, performance, and reliability. As industries increasingly prioritize energy efficiency and sustainability, the demand for hairpin stators is expected to surge, driving innovation and growth in the market.
FAQs
- What are the key advantages of hairpin stator design?
The hairpin stator design offers benefits such as higher power density, improved thermal management, and cost savings due to reduced copper content. - How do hairpin stators contribute to renewable energy generation?
Hairpin stators drive generators in wind turbines and hydroelectric plants, harnessing renewable energy with superior efficiency. - What challenges do manufacturers face in hairpin stator production?
Manufacturers face challenges such as cost constraints, technical complexities in coil winding, and precise insulation application. - What industries utilize hairpin stator technology?
Hairpin stator technology finds applications in automotive propulsion systems, renewable energy generation, and various industrial machinery. - What is the future outlook for hairpin stator manufacturing?
The future of hairpin stator manufacturing looks promising, with advancements in technology and increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions driving growth and innovation.



